BlackRock’s Bitcoin Play: 2024 Performance and Stress Testing
Assessing Bitcoin’s Portfolio Performance in 2024 and Resilience During Market Crises
Exploring Bitcoin’s Portfolio Resilience

BlackRock made waves with its recently published investment case for Bitcoin, “Mega Forces: Sizing Bitcoin in Portfolios.” Advocating for a 2% Bitcoin allocation in traditional portfolios, BlackRock’s thesis emphasizes Bitcoin’s potential as a strategic crypto asset, offering outsized returns, diversification benefits, and manageable risk.
Building on the foundation of our first article, we critically evaluated the impact of a modest Bitcoin allocation. The analysis demonstrated how it enhances portfolio performance and diversification benefits while maintaining a balanced risk profile. However, additional questions demanded further analysis:
What role did Bitcoin play in portfolios during 2024?
How does Bitcoin perform during market downturns?
This second article delves into these critical questions by analyzing Bitcoin’s impact during 2024 and evaluating portfolio performance under stress conditions such as the COVID-19 crash, the 2022 bear market, and the 2023 downturn.
By broadening the scope of our empirical analysis, I aim to provide deeper insights into Bitcoin’s performance under diverse market conditions and critically examine BlackRock’s claims regarding crypto’s role as a strategic asset in modern portfolios.
Missed the first article? Explore my in-depth analysis of BlackRock’s 2% Bitcoin strategy, including its risk-return trade-off and potential as a portfolio diversifier.
2024 Performance in Perspective
The performance of the BlackRock Strategy in 2024 offers key insights into its ability to enhance returns while managing risk compared to the Classic 60/40 Portfolio. By evaluating returns, volatility, and Sharpe ratios, we highlight Bitcoin's impact on portfolio performance over this year.
Did Bitcoin Enhance Returns in 2024?
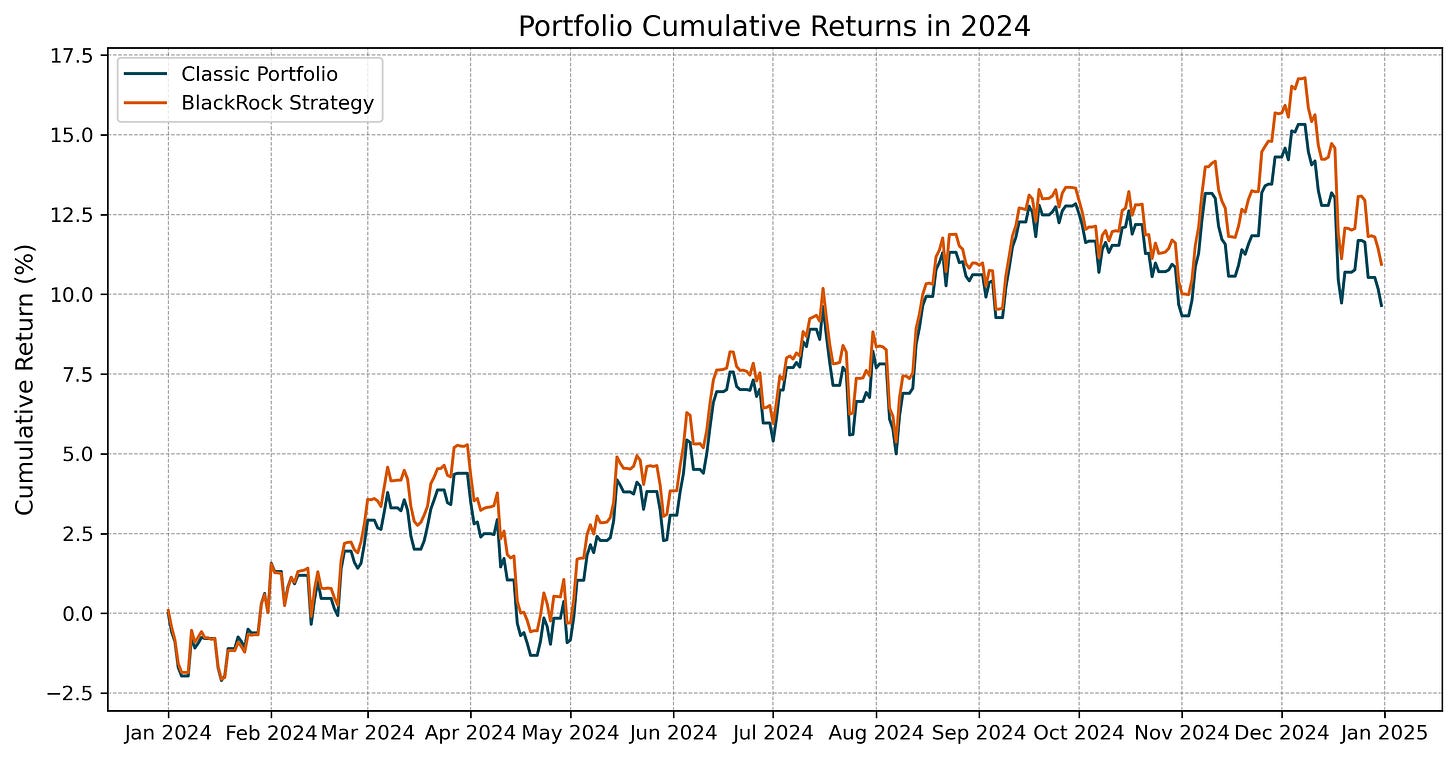
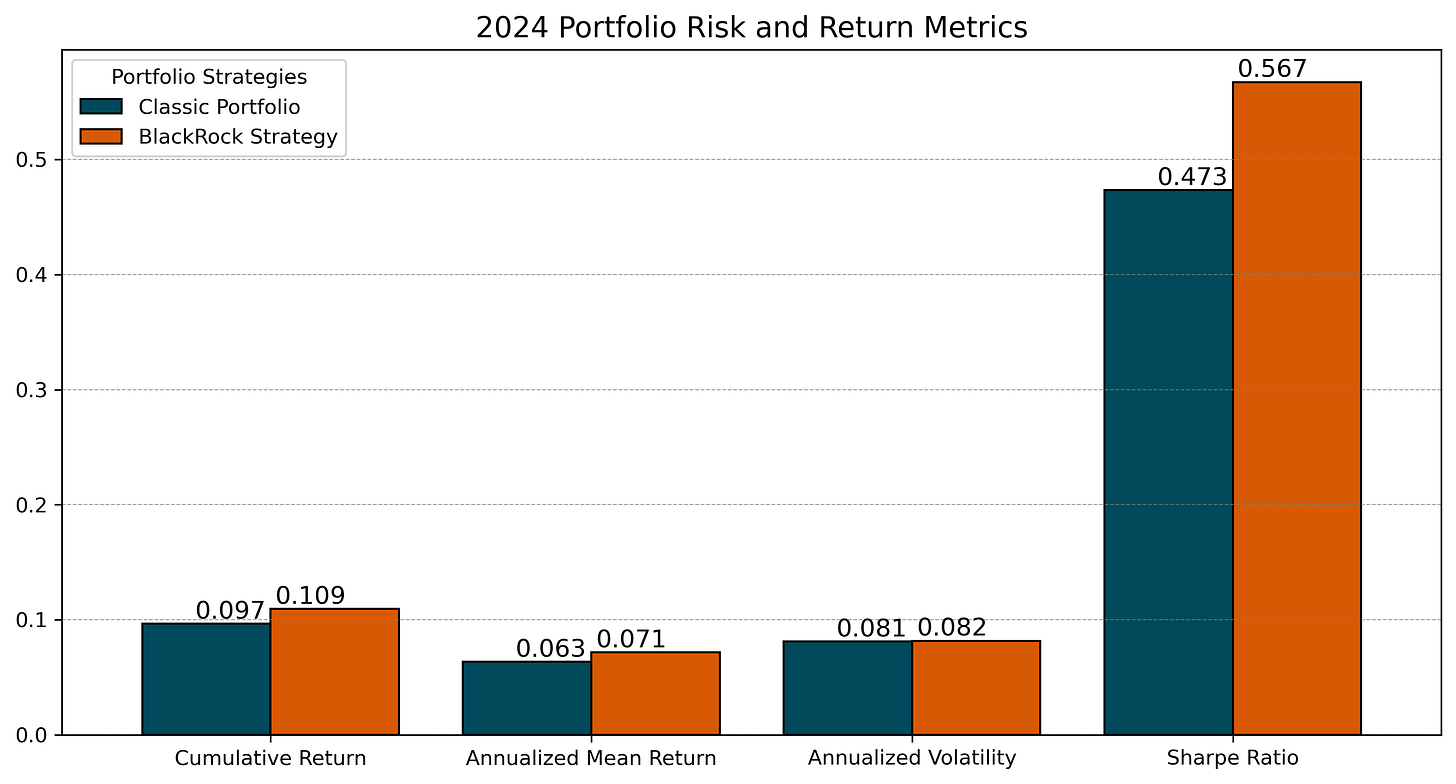
The cumulative returns chart in Figure 1 demonstrates the Bitcoin’s portfolio superior performance compared to the Classic Portfolio in 2024. Notably, BlackRock’s recommended allocation achieved a cumulative return of 10.94%, compared to 9.65% for the classic allocation.
Moreover, the annualized mean returns highlight Bitcoin's contribution as a return enhancer. The BlackRock Strategy yielded an annualized return of 7.1%, outperforming the Classic Portfolio’s 6.3% (see Figure 3). These results demonstrate that even a modest 2% Bitcoin allocation contributed meaningfully to portfolio growth in 2024.
How Did Bitcoin Impact Portfolio Volatility?
Despite Bitcoin's inherent volatility, its 2% allocation resulted in only a minimal increase in overall portfolio risk. The annualized volatility of the BlackRock Strategy reached 8.18%, marginally higher than the Classic Portfolio’s 8.09%, as shown in Figure 3, corraborating previous results over the entire sample period as highlighted in the first article.
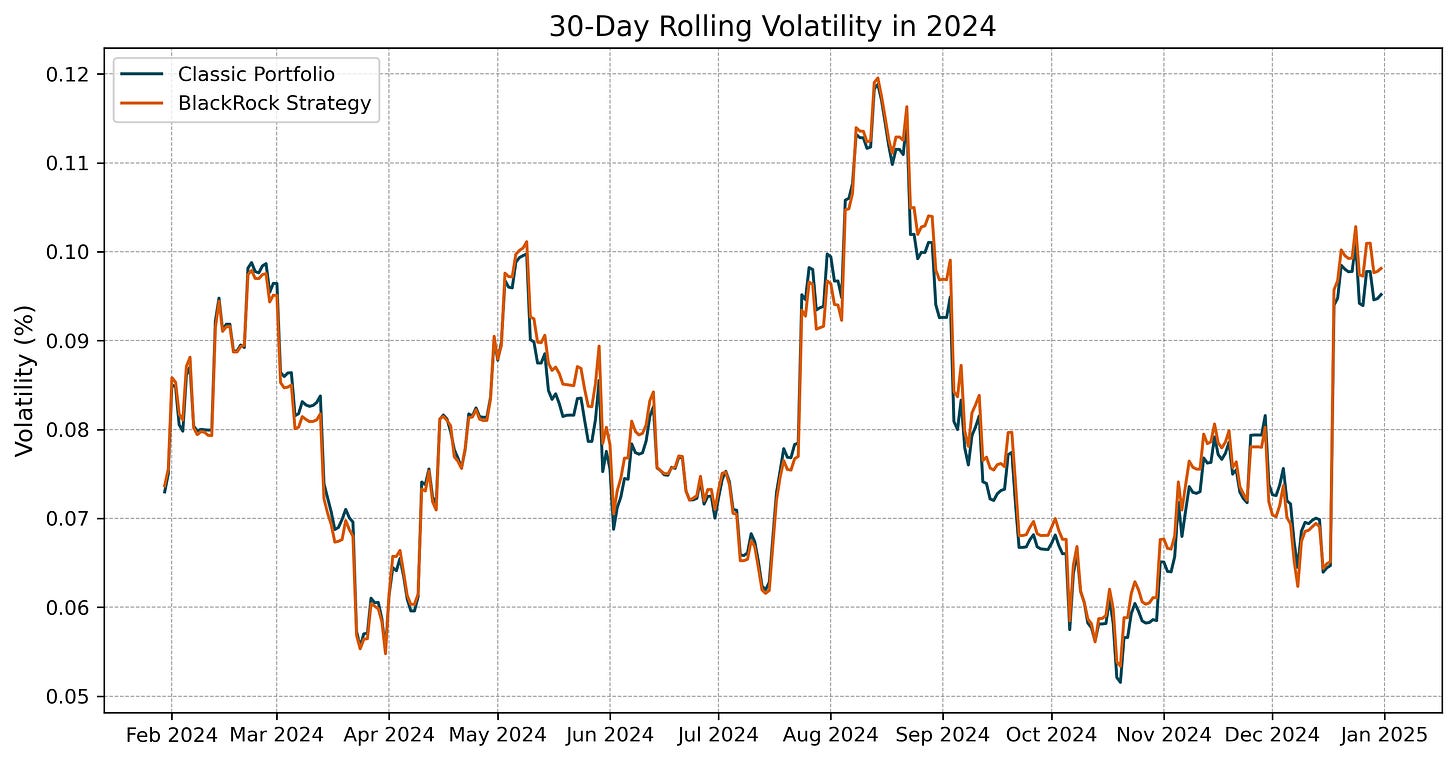
A closer look at the 30-day rolling volatility chart in Figure 2 reveals a similar risk profile for both portfolios throughout 2024. While volatility for the BlackRock Strategy exhibited slightly higher peaks during mid-year turbulence, the difference was negligible, indicating that Bitcoin's inclusion did not materially alter overall portfolio risk.
Did Bitcoin Improve Risk-Adjusted Returns?
The Sharpe ratio, as presented in Figure 2, confirms Bitcoin’s portfolio value from a short-term perspective. Specifically, the BlackRock Strategy achieved a Sharpe ratio of 0.567, significantly higher than the Classic Portfolio's 0.473. This improvement of nearly 20% underscores Bitcoin’s ability to deliver superior risk-adjusted returns, even with a small allocation.
These results reinforce BlackRock’s thesis that cryptocurrencies can enhance returns while managing risk, supporting their case for Bitcoin as a strategic addition to well-diversified portfolios.
Stress Testing the Portfolios
In this section, we analyze the performance of both portfolios during three major market downturns to evaluate whether Bitcoin mitigates or amplifies risk during periods of financial stress: the COVID-19 Crash (February–May 2020), the 2022 Bear Market, and the 2023 Downturn (July–September 2023).
Specifically, we examine cumulative returns, maximum drawdowns and recovery times. The market stress analysis is complemented by a rolling correlation study that uses statistical insights to assess Bitcoin's role as a diversifier during periods of market turmoil.
To What Extent Does Bitcoin Amplify Risk During Crises?
The cumulative returns reveal that the BlackRock Strategy closely mirrored the Classic Portfolio during all three stress periods. However, slight variations suggest that Bitcoin had a marginally amplifying effect on risk:
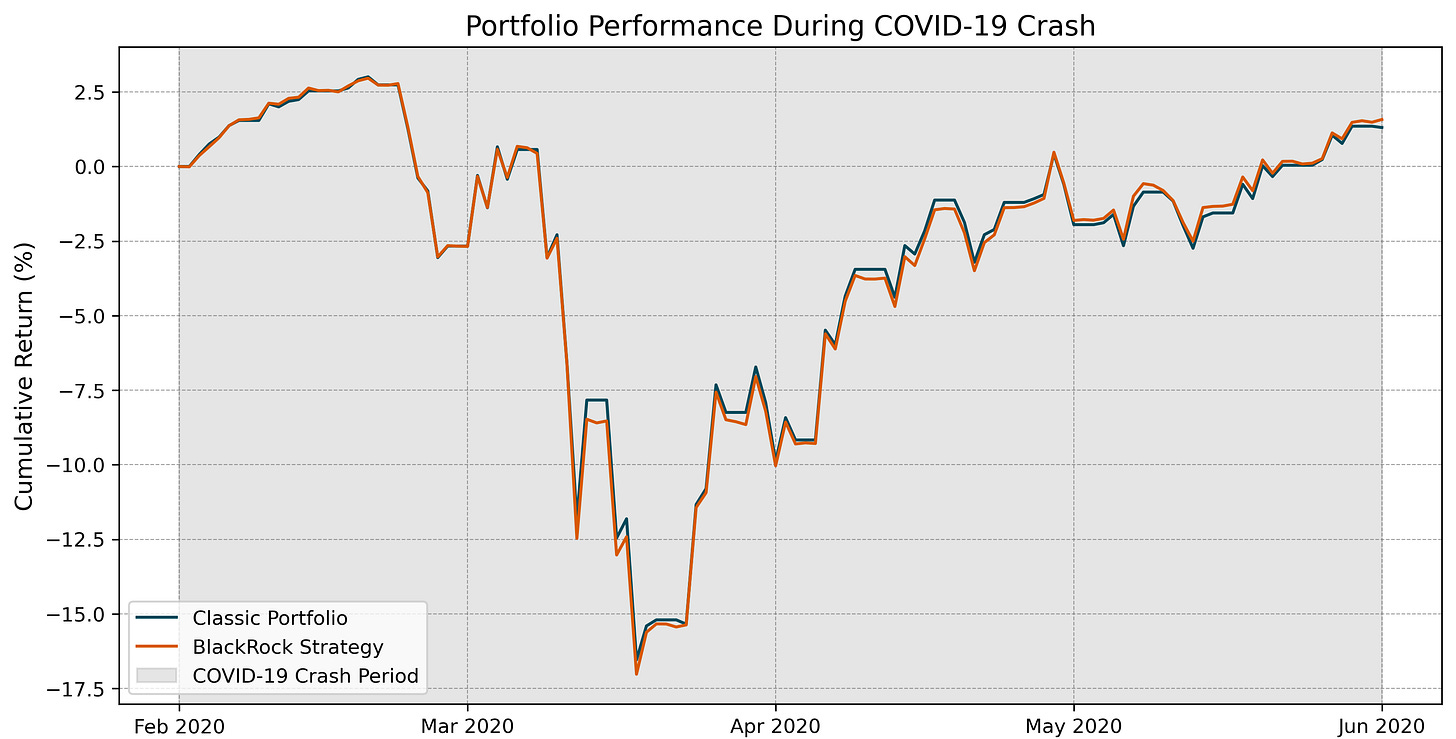
COVID-19 Crash: Both portfolios experienced significant drawdowns, with maximum losses of -19.0% for the Classic Portfolio and -19.4% for the BlackRock Strategy. Neither portfolio fully recovered within the observed timeframe, indicating prolonged stress effects.
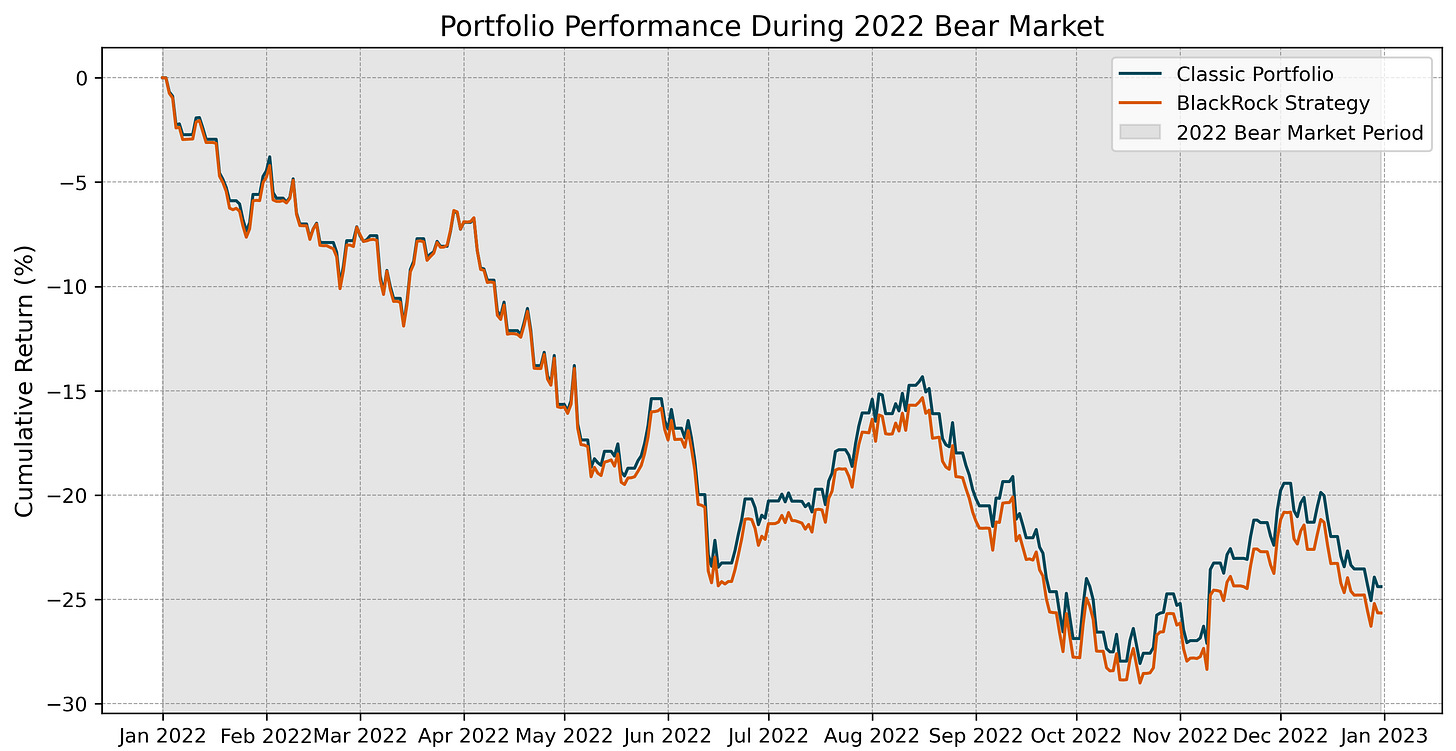
2022 Bear Market: The BlackRock Strategy faced a slightly higher drawdown (-29.0%) compared to the Classic Portfolio (-28.1%). Both portfolios showed resilience post-crisis but failed to recover fully by the end of the period.
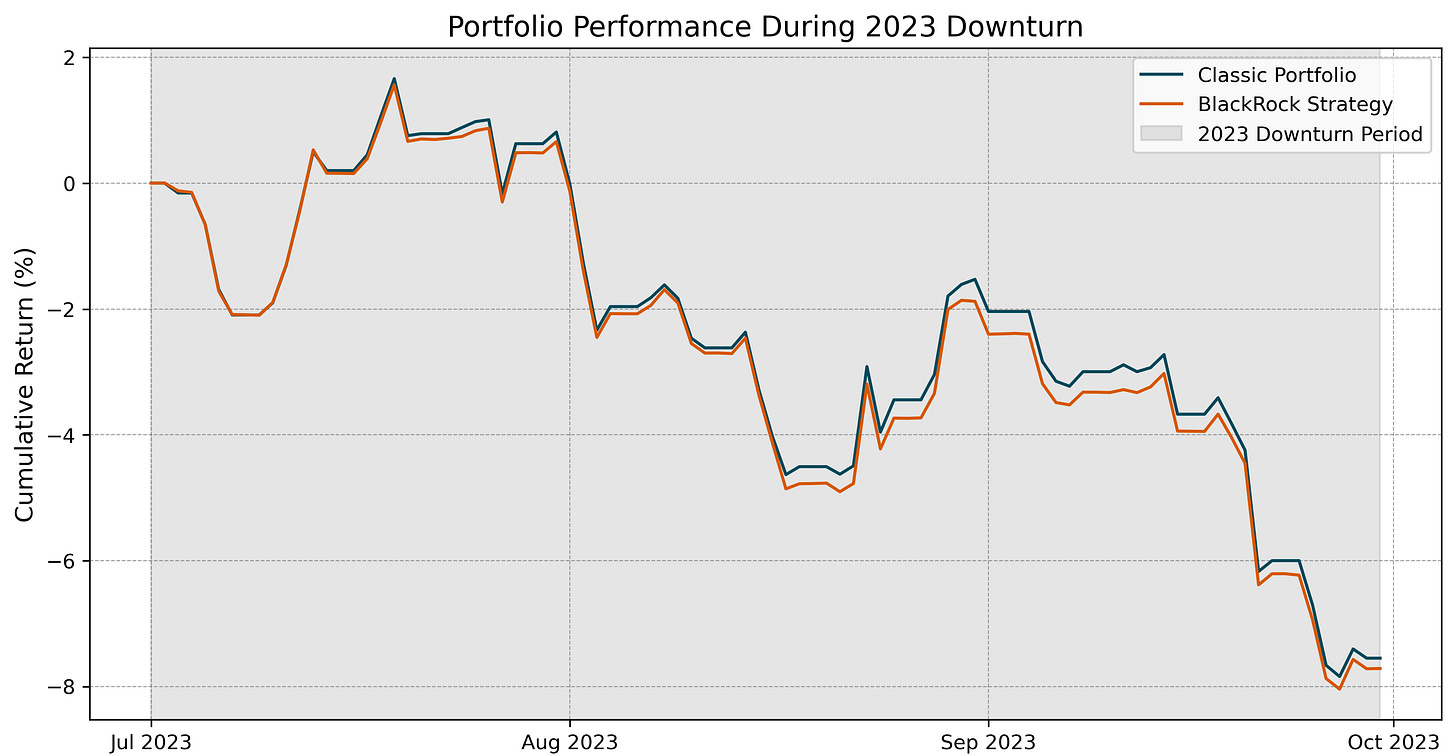
2023 Downturn: Bitcoin’s inclusion marginally increased maximum drawdowns, with the BlackRock Strategy falling -9.5% compared to -9.3% for the Classic Portfolio. However, both portfolios displayed similar trajectories, reflecting limited divergence.
How Does Bitcoin Correlate With Traditional Assets During Market Shocks?
To provide deeper insights into Bitcoin's role as a diversifier during periods of financial stress, we analyze its correlations with key asset classes, including S&P 500, US Bonds, and gold. Presenting correlations within each stress period offers a contextual understanding of Bitcoin’s performance under specific market conditions.
COVID-19 Crash
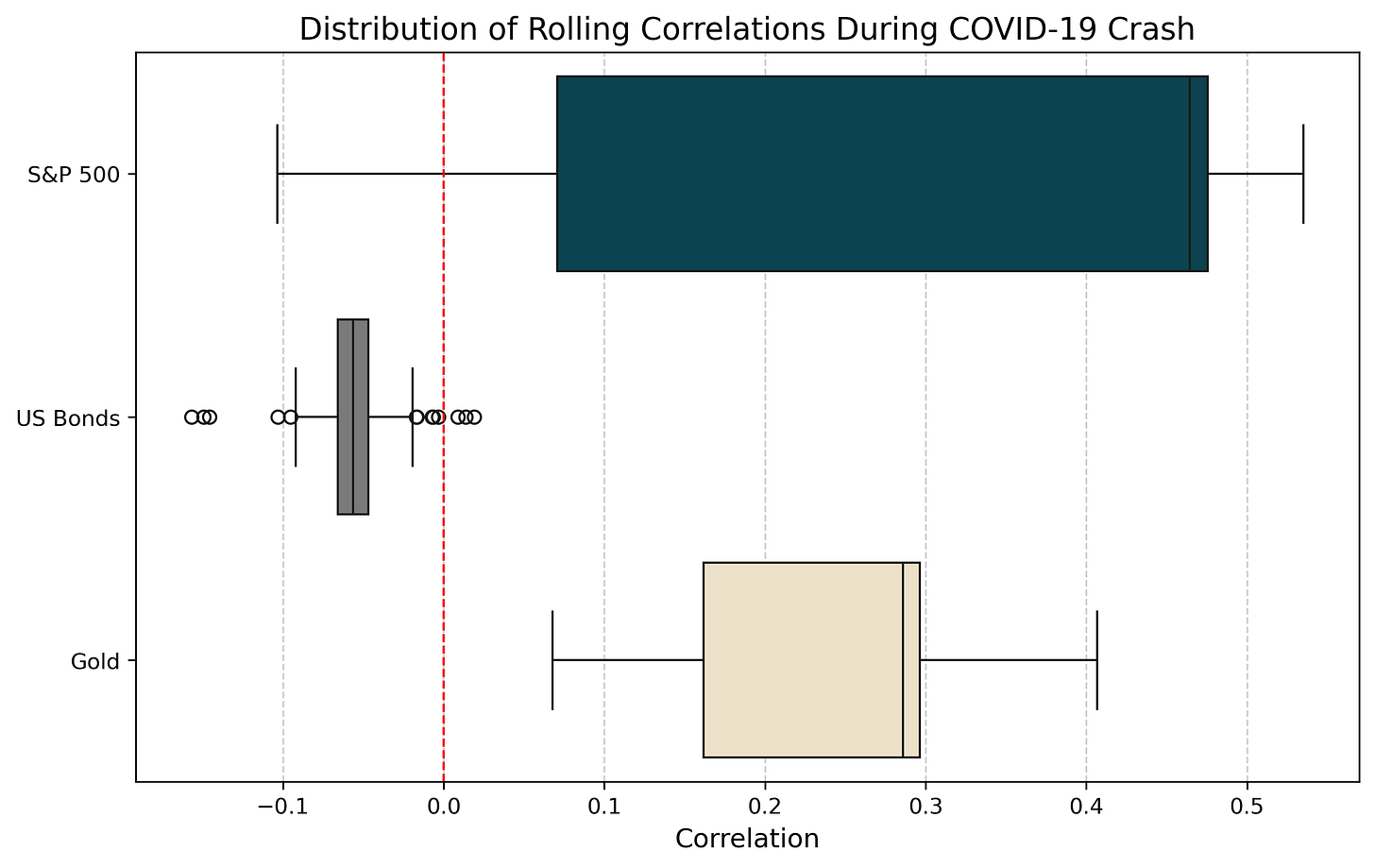
During the COVID-19 Crash, Bitcoin’s correlation with traditional assets fluctuated widely, reflecting its dynamic behavior under extreme stress:
S&P 500: Bitcoin exhibited an average correlation of 0.317, but the correlation ranged significantly, from as low as -0.104 to as high as 0.535. This variability (standard deviation of 23.2%) highlights its partial alignment with equity markets during risk-on phases while retaining some independence.
US Bonds: Correlations with bonds remained slightly negative (-0.056 mean correlation) with very low variability, providing potential diversification benefits for portfolios dominated by fixed-income securities.
Gold: Bitcoin’s average correlation with gold was 0.243, indicating a moderate positive alignment. This suggests that Bitcoin may partially behave as a store of value during crisis periods, though not as strongly as traditional safe-haven assets like gold.
2022 Bear Market
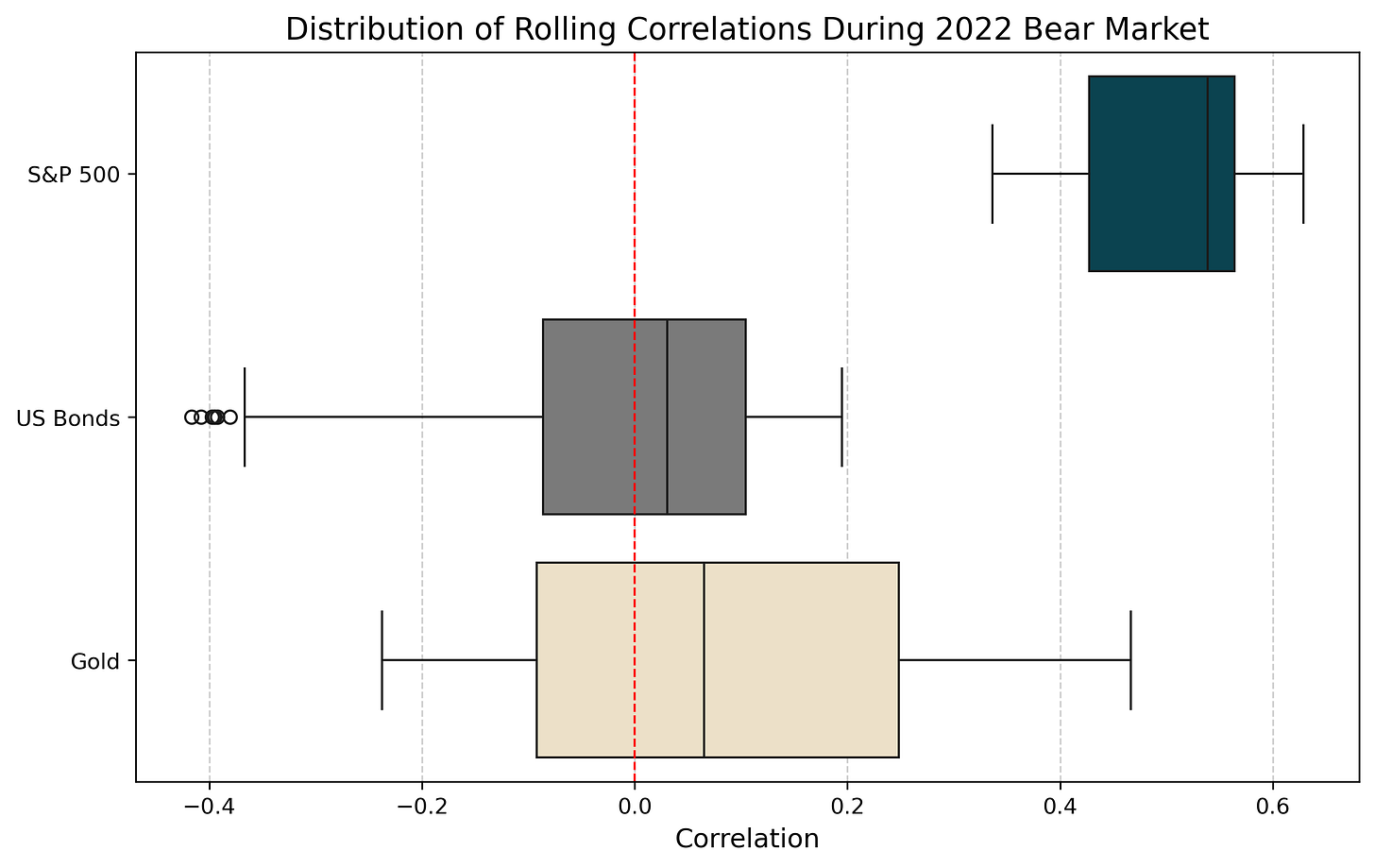
The 2022 Bear Market was characterized by elevated correlations between Bitcoin and equities, likely due to a more risk-on environment (particularly triggered by major busts like the Terra Luna Crash and the FTX scandal) and tighter monetary conditions:
S&P 500: Bitcoin’s correlation with equities increased substantially, with a mean of 0.504 and a narrow interquartile range, reflecting its stronger co-movement with risk assets.
US Bonds: Bitcoin exhibited negative correlations with bonds, with a low of -0.417, averaging -0.008. This decoupling underscores Bitcoin’s diversification potential in portfolios exposed to fixed-income instruments during rising-rate environments.
Gold: Bitcoin’s correlation with gold was weaker, averaging 0.088, diverging it from traditional hedging assets. Notably, gold exhibited the highest variation (standard deviation of 19.5%) compared to equities and bonds throughout 2022.
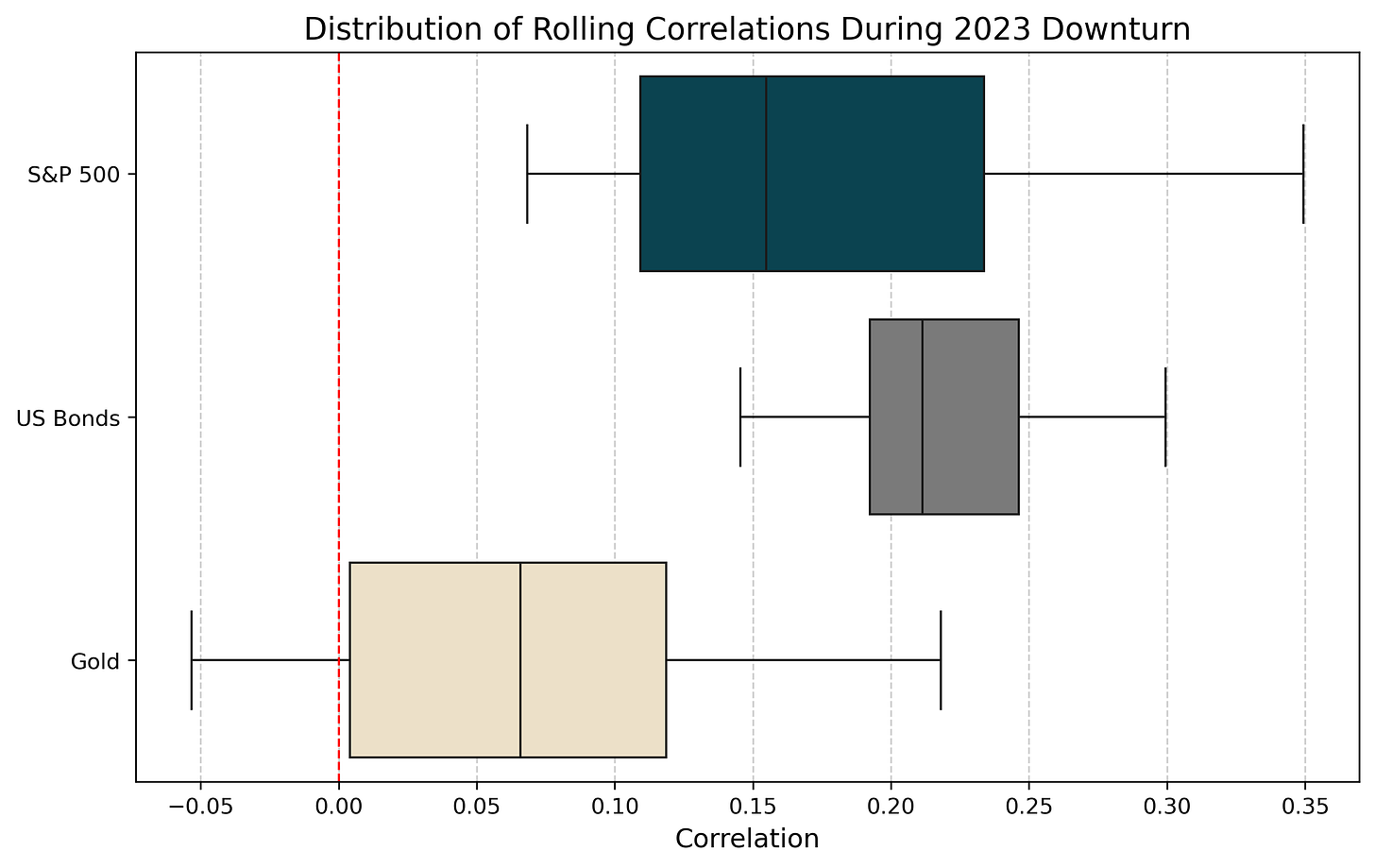
2023 Downturn
During the 2023 market downturn, Bitcoin exhibited more moderate, positive correlations with traditional assets, suggesting its evolving role as a portfolio diversifier:
S&P 500: Correlations with equities were muted, with a mean of 0.178, indicating greater independence during short-term market downturns.
US Bonds: Bitcoin exhibited a moderate positive correlation with bonds, averaging 0.219, suggesting that during market downturns, Bitcoin and bonds share greater co-movement compared to periods of acute shocks, such as the COVID-19 crisis, or prolonged bear markets as in 2022.
Gold: Bitcoin's correlation with gold remained close to zero (mean of 0.064), reflecting minimal alignment during this short-term period of distress.
Bitcoin's correlation during stress periods highlights its context-dependent diversification value. During prolonged downturns, such as the 2022 Bear Market, Bitcoin showed a stronger alignment with equities, reflecting its partial risk-on nature. In contrast, during short-term shocks like the COVID-19 crash, its correlations with bonds turned negative, suggesting countercyclical behavior. Correlations with gold remained weak across all periods, reaffirming Bitcoin’s divergence from traditional safe-haven assets.
These patterns underscore Bitcoin’s situational diversification benefits, which depend on broader market dynamics.
Preliminary Findings and Insights
In this second article, we addressed two key questions to evaluate Bitcoin’s role in portfolio resilience and stress scenarios:
1. What Role Did Bitcoin Play in Portfolios During 2024?
The analysis highlights Bitcoin’s continued contribution to portfolio performance in 2024. The BlackRock Strategy achieved a cumulative return of 10.94% compared to 9.65% for the Classic Portfolio. Furthermore, the Sharpe ratio for the BlackRock Strategy reached 0.567, demonstrating superior risk-adjusted returns despite a marginal increase in volatility.
Bitcoin’s inclusion provided incremental performance advantages in a relatively stable year, supporting BlackRock’s thesis that even a modest allocation can enhance returns without significantly increasing portfolio risk.
2. How Does Bitcoin Perform During Market Downturns?
The stress test analysis revealed that Bitcoin’s inclusion slightly amplified drawdowns during major market downturns, such as the COVID-19 crash (-19.4% vs. -19.0% for the Classic Portfolio) and the 2022 bear market (-29.0% vs. -28.1%). However, the BlackRock Strategy exhibited resilience comparable to the Classic Portfolio across all three stress periods.
Bitcoin’s correlations with traditional assets varied significantly across stress scenarios, underscoring its context-dependent diversification potential. During the COVID-19 crash, Bitcoin's negative correlation with bonds (-0.056) provided diversification benefits, while its partial alignment with equities (average 0.317) reflected dynamic risk-on behavior.
In the 2022 bear market, Bitcoin’s correlation with equities strengthened to 0.504, indicating increased alignment with risk assets, while its bond correlation (-0.008) remained weak.
The 2023 downturn showed more muted correlations with equities (0.178) and moderate alignment with bonds (0.219), highlighting greater independence in shorter-term market disruptions.
Overall, Bitcoin’s performance during stress periods underscores its situational diversification benefits, with its impact heavily influenced by market conditions.
Looking Ahead
While this analysis has provided deeper insights into Bitcoin’s performance during recent market and stress periods, the question of larger allocations remains unanswered:
What are the implications of increasing Bitcoin’s allocation to 5%, 10%, or even 20%?
To what extent can we validate or reject BlackRock’s claims about Bitcoin’s role in portfolio construction?
These questions will be the focus of our next article, where we will evaluate Bitcoin allocation scenarios beyond 2% and synthesize findings from the empirical analysis.